MARKET RESILIENCE SUPPORTED BY DOVISH FEDERAL RESERVE
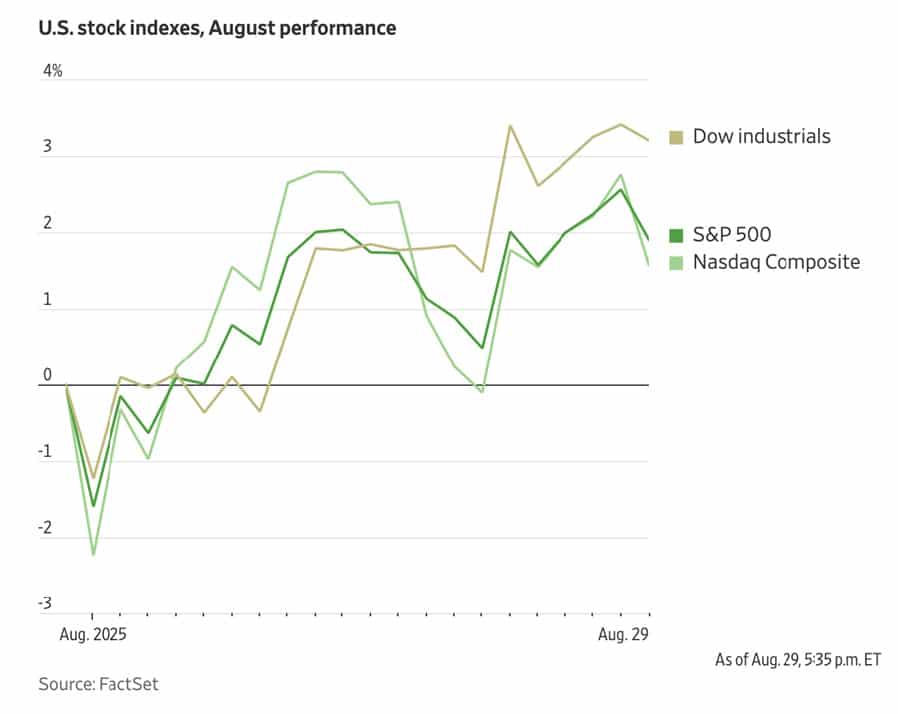
Equity markets notched up fresh records during August despite emerging headwinds that tested investor confidence. During the month, investors navigated a delicate balance between robust corporate earnings, evolving monetary policy expectations, and global economic and geopolitical structural shifts.
TREASURY VOLATILITY MEASURED BY THE MOVE INDEX HIT ITS LOWEST LEVEL IN THREE YEARS
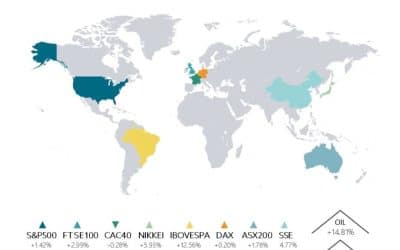
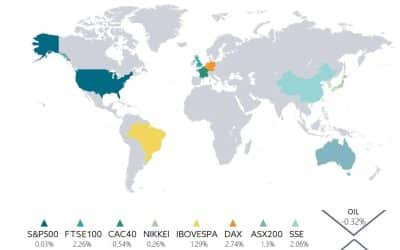
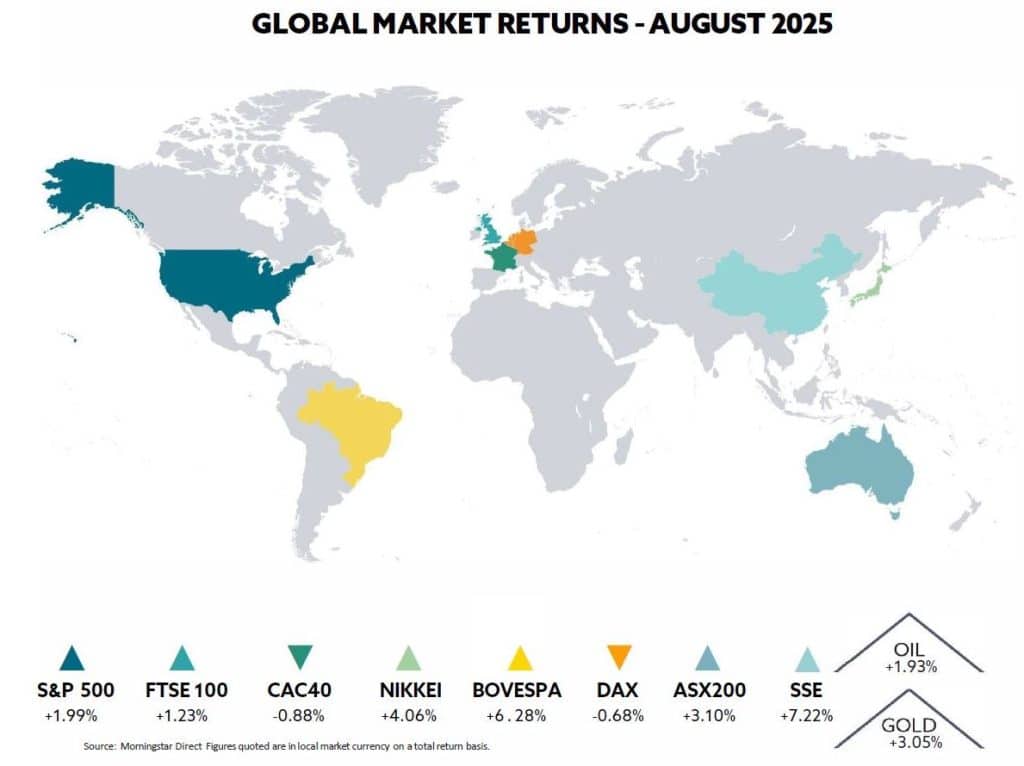
In the US, the S&P 500 advanced 1.9% for its fourth consecutive monthly gain. The index’s performance underscored sustained investor appetite for risk assets. The Nasdaq Composite increased by 1.6%.
The FTSE 100 added 1.2% for month and is 15.6% higher year to date while the Eurostoxx 50 rose 0.9% and is ahead 8.1% ahead year to date. China’s CSI 100 surged 10.3%, leaving it 15% ahead year to date, while the Nikkei gained 4.1% and is up by 8.3% year to date.
The “Magnificent Seven” technology giants continued to lead the market, generating a collective 5.6% return that lifted broader large-cap indices. This performance was particularly noteworthy given the headwinds facing growth stocks from valuation concerns.
Fixed-income markets presented a more mixed picture. The Bloomberg US Aggregate Bond Index declined modestly by 0.3% as the 10-year Treasury yield climbed from 4.24% to 4.37%. However, investment-grade corporate bonds managed to eke out a small 0.1% gain, suggesting credit markets remained supportive despite duration concerns. Surprisingly, Treasury volatility measured by the MOVE index hit its lowest level in three years, signalling unusually calm bond market conditions even amid global uncertainty.
INFLATION DATA SHOWED THE FED’S FAVOURED PCE INFLATION MEASURE HELD STEADY AROUND 2.6%
Commodities’ performance was also mixed, with Brent crude falling 6.1%, closing at around $68 per barrel. In contrast, precious metals maintained their appeal as portfolio hedges, with gold stabilising above $3,300 per ounce before moving higher while silver and platinum gained ground, supported by industrial demand and improving investment sentiment.
The month’s key economic catalyst centred on evolving Federal Reserve policy expectations. Inflation data showed the Fed’s favoured PCE inflation measure held steady around 2.6%, matching forecasts and reinforcing market expectations for monetary easing. Fed Chair Powell’s Jackson Hole remarks were interpreted as dovish, with his emphasis on labour market risks increasing the probability of a September rate cut to 89% according to Fed funds futures.
FED CHAIR POWELL’S JACKSON HOLE REMARKS WERE INTERPRETED AS DOVISH, WITH HIS EMPHASIS ON LABOUR MARKET RISKS
Labour market softening provided the clearest signal of economic deceleration during the month. July payrolls rose by just 73,000 jobs, significantly below expectations, while substantial downward revisions to prior months revealed the weakest labour data since the pandemic era. This employment weakness, combined with controlled inflation dynamics, created the conditions for the Fed’s anticipated policy pivot toward accommodation.
PROFIT-TAKING IN AI STOCKS REPRESENTS TEMPORARY PAUSE
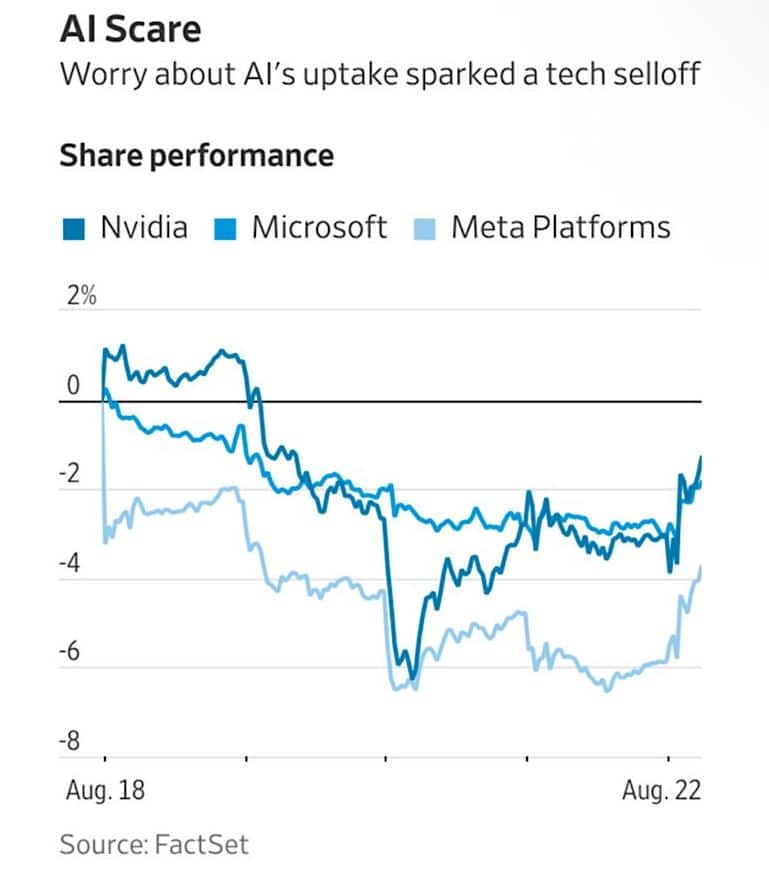
The late-August weakness in AI and technology stocks reflected a natural consolidation after gains rather than a fundamental shift in the sector’s growth trajectory. The main AI beneficiaries to date, including Nvidia, Broadcom, Dell, and Oracle, experienced notable selling pressure as investors locked in profits.
Several factors contributed to investors taking profits. Earnings season circumspection played a role, as markets had priced in near-flawless growth trajectories, making even slight management caution a catalyst for selling. Valuation concerns became increasingly prominent, with forward price-to-earnings multiples reaching well above historical averages across the sector. The temporary spike in Treasury yields mid-month, before Powell’s dovish Jackson Hole comments, pressured high-growth names with valuations sensitive to discount rate assumptions.
Portfolio manager sector rotations also saw capital shift from AI leaders into cyclical and defensive sectors, including energy, industrials, and consumer staples. This rebalancing was a result of prudent risk management rather than concerns about AI’s fundamental prospects.
HYPERSCALER CAPITAL SPENDING IS EXPECTED TO ACCELERATE INTO 2026
Multiple factors support the view that this represents a temporary lull rather than a secular turning point. Structural demand for AI continues accelerating, with enterprise adoption of AI tools, growth in AI-driven cloud workloads, and rising semiconductor infrastructure investment continuing to provide multi-year growth tailwinds. Corporate earnings continue to show resilience, with profit margins at leading AI firms well above average while hyperscaler capital spending is expected to accelerate into 2026.
Recovery prospects are also supported by the sector’s liquidity advantage. Large-cap technology stocks remain the most liquid and defensive growth investments available to institutional investors, meaning price declines tend to attract buyers quickly. Most strategists maintain bullish outlooks for the sector, viewing the August weakness as healthy consolidation that positions these companies for renewed outperformance into year-end.
RISING UK GILT YIELDS SIGNAL MULTIPLE RISKS
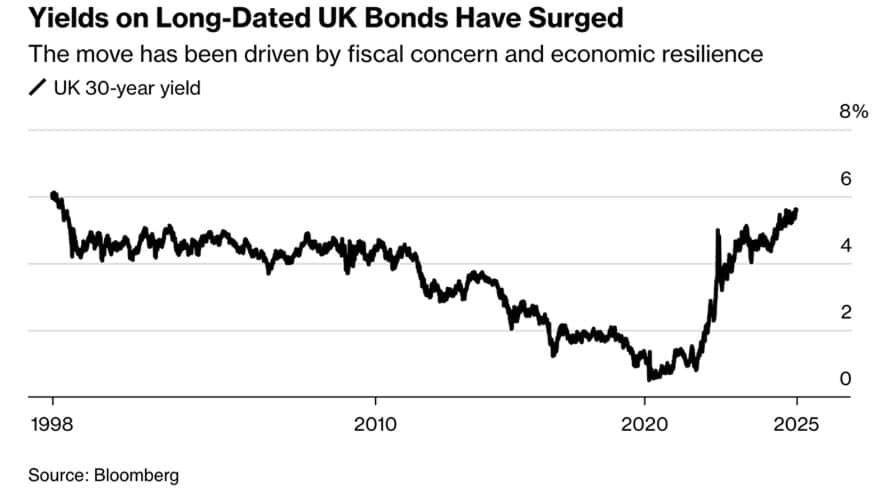
The dramatic rise in UK government bond yields in August highlighted pressure onBritain’s fiscal position and concerns about monetary-policy coordination. Ten-year gilts hit ~4.7% while thirty-year yields climbed to ~5.6%, levels likely to constrain government spending flexibility and signal investor wariness about the UK’s economic trajectory.
Multiple factors were behind the bond market sell-off. Inflation at 3.8% in July, well above the BoE’s 2% target, reduced hopes for aggressive easing. A split BoE vote, with four members preferring to hold rates steady rather than cut, reinforced a hawkish shift and disappointed investors who had priced in more accommodation. Eroding confidence in fiscal discipline widened risk premiums on UK debt. Concerns over public sector spending trajectories, policy reversals and adherence to fiscal rules intensified doubts about debt sustainability. This scepticism revived memories of the Liz Truss mini-budget, when bond vigilantes forced the government to take fiscal policy action by putting pressure on bond markets.
DECLINING CONFIDENCE IN FISCAL DISCIPLINE WIDENED RISK PREMIUMS ON UK GOVERNMENT DEBT
The global wind-down of central bank QE programs increased issuance from multiple sovereigns, creating supply-demand imbalances and adding another headwind to the UK bond market. Elevated yields pose risks for policymakers and investors. Higher borrowing costs lift already heavy debt-servicing, potentially forcing spending cuts or tax rises that may undermine growth. Long-duration gilts are vulnerable, with bonds issued in low-rate periods suffering sharp declines. Market liquidity concerns have also emerged as a result of reduced institutional investor interest, adding to the bond market’s vulnerability.
However, some analysts view current yields as attractive entry points for patient investors, particularly if fiscal discipline improves and inflation moderates.

 HELPLINE:
HELPLINE: